Designed to achieve the hat trick of LEED Platinum, LEED Zero Carbon, and WELL Building Gold
By John Gillanders
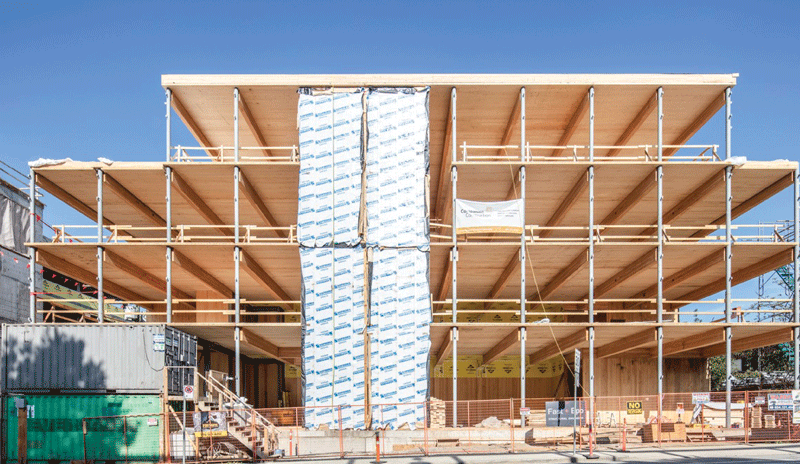
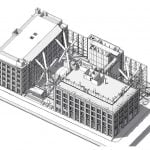
Portland Commons is a high-performance commercial office and retail development, integrating with the surrounding neighbourhood through its preservation of surrounding heritage buildings, terraced massing and activated, pedestrian focussed street presence.
By contributing high-quality employment and retail spaces, this project strengthens the economic and social fabric of an important mixed-use district, just steps from the planned Front and Spadina GO and commuter rail station.
The Project is designed to achieve LEED Platinum (Core + Shell), LEED Zero Carbon, and WELL Building Gold standards, supporting the highest levels of energy efficiency, environmental responsibility, and occupant physical and mental well-being through access to outdoor terraces, biophilic elements, and abundant natural light.
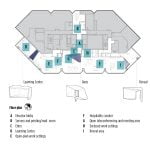
Thirteen landscaped tenant terraces, green roofs, and native plantings enhance local biodiversity while reducing the urban heat island effect. Stormwater management strategies include permeable surfaces and rainwater harvesting to support sustainable greywater use within the site.
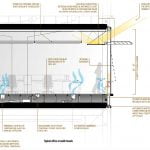
Floor-to-ceiling glazing provides occupants with unrestricted panoramic views and deep sunlight penetration. In addition, more than 90% of the occupied spaces have direct access to an operable window supporting natural ventilation and occupant comfort. The HVAC system employs MERV 13 filters and bipolar ionization to maintain superior indoor air quality while reducing energy consumption.
The underfloor (UFAD) HVAC system allows all occupants personal control of temperature and fresh air with individual manually operated diffusers. The UFAD system follows a “one pass” airflow approach that supports occupant health by delivering fresh air at the floor and drawing it away at the ceiling, eliminating the mixing of fresh and stale air in the space.
Amenities such as spa-like “end-of-trip” facilities, comfortable and secure bicycle storage, and touchless building controls further enhance the user experience.
Portland Commons integrates low-flow plumbing fixtures, water-efficient landscaping, and a rainwater harvesting system to minimize potable water consumption. The project achieves a 47% reduction in water use compared to baseline models.
The building employs Enwave’s Deep Lake Water Cooling system, underfloor air distribution, and a high performance building envelope to minimize energy demand. Annual heating and cooling energy intensity is 137 kWh/m² or less, with a strong emphasis on reducing reliance on fossil fuels. The HVAC system allows for up to a 25% reduction in outside air conditioning, and the supply air temperature requires less cooling: to 17-18 degrees Celsius rather than the traditional office building standard of 12-14 degrees Celsius. This allows for longer free-cooling periods that can extend into the late spring and start in early fall, reducing the cooling energy used by 26.8% compared to a typical office building.
PROJECT TEAM
- OWNER/DEVELOPER Carttera Private Equities Inc.
- ARCHITECT Sweeny&Co Architects Inc
- GENERAL CONTRACTOR EllisDon Corporation
- LEASING TEAM JLL
- LANDSCAPE ARCHITECT NAK Design Strategies
- CIVIL ENGINEER MGM Consulting Inc.
- STRUCTURAL ENGINEER RJC Engineers
- MECHANICAL ENGINEER TMP (The Mitchell Partnership & BPA) Consulting Engineers
- ELECTRICAL ENGINEER Mulvey & Banani International Inc.
- VERTICAL TRANSPORTATION Soberman Engineering
- ENERGY CONSULTANT Ecovert
- MANAGEMENT AND CONSULTING SERVICES FOR CONSTRUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT Cavendish Management
- PHOTOS Gus Sarino
PROJECT PERFORMANCE
- Energy intensity (heating and cooling) 137KWhr/m2/year
- Energy intensity reduction relative to reference building under MNECB 1997 26.8%
- Reduction in water consumption relative to reference building under LEED 47%
- Recycled material content by value 46.8%
Part of the exterior cladding consists of Vicwest Channel Wall . Interior finished include Quebec Mosaic, Quartz Jambs and Granite Stone by Olympia Tile+Stone and CertainTeed Type X and Acoustic Gypsum Board.
JOHN GILLANDERS IS A PARTNER AT SWEENY&CO (ARCHITECTURAL PRINCIPAL-IN-CHARGE ON PORTLAND COMMONS).
SUBSCRIBE TO THE DIGITAL OR PRINT ISSUE OF SABMAGAZINE FOR THE FULL VERSION OF THIS ARTICLE.